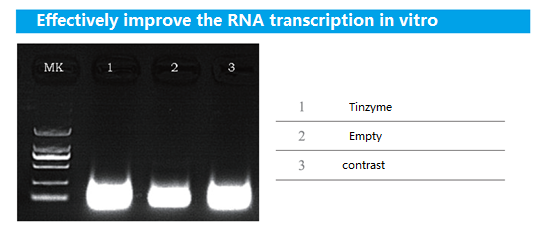
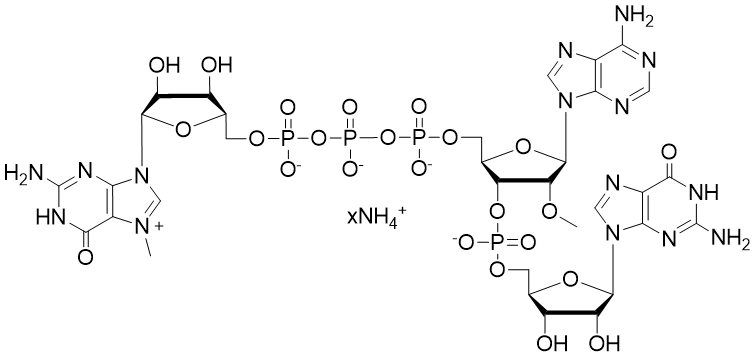
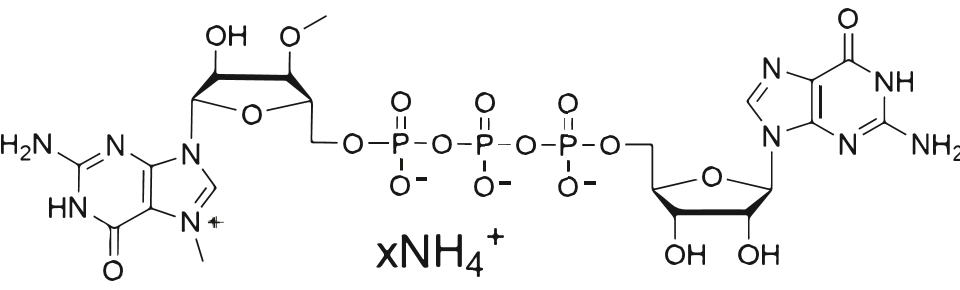
Vaccinia Capping Enzyme
2022-09-15
HotVent exo- DNA Polymerase
2022-09-15Description
Ribonuclease R (RNase R), derived from the E. coli RNR superfamily, is a magnesium ion dependent 3 ‘- 5’ ribonuclease that can gradually cut RNA into dinucleotides and trinucleotides from the 3 ‘- 5′ direction. RNase R can digest almost all linear RNA, but it is difficult to digest circular RNA, Lasso structure RNA and short double stranded RNA molecules with less than 7 nucleotides protruding from the 3’ end.
RNase R is often used in gene expression and variable splicing studies. It can digest linear RNA to enrich circular RNA or lasso structure RNA.
Applications
1. Gene expression research;
2. Variable shear study;
3. Enriching circrnas from biological samples;
4. RNA that recognizes intronic lasso structure;
5. Identification of exonic circrnas.
Storage buffer
50 mM Tris-HCl, 100mM NaCl, 0.1mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, 0.1% Triton® X-100 and 50% Glycerol(pH 7.5 at 25 ℃)
Storage Condition
Store at -20 °C to avoid repeated freezing and thawing
Unit Definition
The enzyme required to convert 1 µ g poly (a) into acid soluble nucleotides in 10 minutes under standard reaction conditions at 37 °C was defined as 1 U
Component
| RNase R(20 U/μl) | 25 μl |
| 10× RNase R Buffer | 1 ml |
| RNase Free Water | 1 ml |
Note
1) Before the experiment, the workbench shall be cleaned and the required RNase free materials shall be prepared to reduce or eliminate the residual effects of RNase such as solution, EP tube and tip used in the laboratory;
2) 0.1-1.0 mM Mg2+ is required for RNase R activity;
3) With the increase of substrate RNA, the digestion time could be prolonged and the amount of enzyme increased;
4) Some circrnas or lasso structure RNAs will reduce their abundance after being digested by RNase R for a long time, which may be due to their weak resistance to RNase R digestion;
5) EDTA can affect the activity of RNase R.
Order
| RR01 | RNase R | Ribonuclease R, R&D Grade |